Never miss an update from Kyoto University
Create your free account to connect with Kyoto University and thousands of other innovative organizations and professionals worldwide
Background
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are a promising low-cost-per-watt solar technology that has soared in efficiencies from 4% to 26% in the last decade. PSCs include a Perovskite layer composed of a ABX3 crystal-structured hybrid organic–inorganic material sandwiched between several other layers. PSCs are thin, light, flexible, cheap, and easy to produce. However, durability, scaling up, and the inclusion of a toxic metal lead as a component of perovskite materials are major bottlenecks precluding commercial-sized production of PSCs.
Technical Summary
The present invention is a mixed ultrathin tin-lead-based film for PSCs. The researchers made a highly purified tin-containing perovskite semiconductor material by partially replacing lead with tin.EDAI2 solution is used for the post-treatment of the perovskite top surface which has a polishing effect, washing away the surface layer of the perovskite film. The addition of GlyHCl ensures improved crystallinity and reduced defect densities at the bottom region.The application of a thin film increased the power conversion efficiency of PSCs to 23.6%.
➤Even coating is achieved
The material is applied by a low-temperature wet coating process allowing for a highly uniform ultrathin film as shown in Fig. 1. The researchers plan to switch to roll-to-roll production that can be tailored to different applications and manufacturing scale in the future.
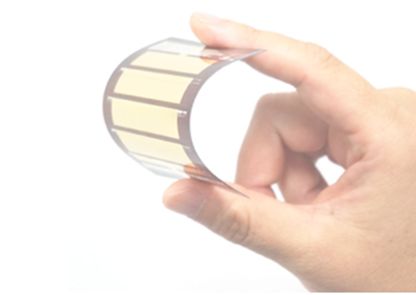
Figure 1. The low-temperature wet coating ensures ultrathin uniform film application.
➤ Durable for indoor usage
The inventors have cleared the 10-year durability requirement for indoor usage of the PSCs. They are currently testing PSC-equipped IoT CO2 sensor terminals inside Tokyo Metropolitan Government facilities. Further R&D is required to optimize durability for outdoor usage of PSCs.
EneCoatis a spin-off from Kyoto University that develops PSCs for portable solar power supplies and IoT devices.
Technology Readiness Level
5
Potential Applications
Possible Collaboration Mode(s)
Patent No
WO2021182431
Publication(s)
Hu S, Otsuka K, Murdey R, Nakamura T, Truong MA, Yamada Tet al. Optimized carrier extraction at interfaces for 23.6% efficient tin–lead perovskite solar cells.Energy Environ Sci 2022;15: 2096–2107.
Ohashi N, Kaneko R, Sakai C, Wasai Y, Higuchi S, Yazawa Ket al. Stress-Compensated, Deformation-free Indium Tin Oxide Bilayer Electrodes for Ultrathin Flexible Perovskite Solar Cells. 2023. doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-2426805/v1.
Kyoto University was founded in 1897, the second university to be established in Japan. Kyoto University is among 10 National Designated Universities in Japan. It boasts 18 graduate schools, 10 faculties, 12 research institutes, and 26 centers and other establishments. Research conducted at Kyoto University spans the full spectrum of fields from social to natural science.
The outstanding research conducted at Kyoto University gives birth to useful technologies that could greatly benefit society. IAC (Office of Institutional Advancement and Communications) was established at Kyoto University to bridge the gap between researchers and industry. We facilitate joint research, technology transfer, creation of university startups, and provide entrepreneurial education. We are building a strong network of global industry partners to make sure basic research reaches the market.
Create your free account to connect with Kyoto University and thousands of other innovative organizations and professionals worldwide
Send a request for information
to Kyoto University
Technology Offers on Agri-Food are directly posted
and managed by its members as well as evaluation of requests for information. Agri-Food is the trusted open innovation and science network aimed at directly connect industry needs with professionals online.
Need help requesting additional information or have questions regarding this Technology Offer?
Contact Agri-Food support