Airable has synthesized a soy-based antistatic additive (ASA) for polyurethane coatings, which are inherently electrically insulative. ASAs are added to materials to reduce or eliminate static electricity, which may be desirable for aesthetics, safety, or product performance, depending on the application. The Airable product has broad applicability, from painting in the house to industrial mold presses.
Overview
Airable Research Lab has synthesized a soy-based antistatic additive (ASA) for polyurethane coatings, which are inherently electrically insulative. When a conductive medium comes into contact with a polyurethane coating, an electric shock will transfer from the coating to the conductive material. The sudden release of electricity can be a fire risk and may damage electronic devices.
ASAs are added to materials to reduce or eliminate static electricity, which may be desirable for aesthetics, safety, or product performance, depending on the application. The Airable product has broad applicability, from painting in the house to industrial mold presses.
The Technology
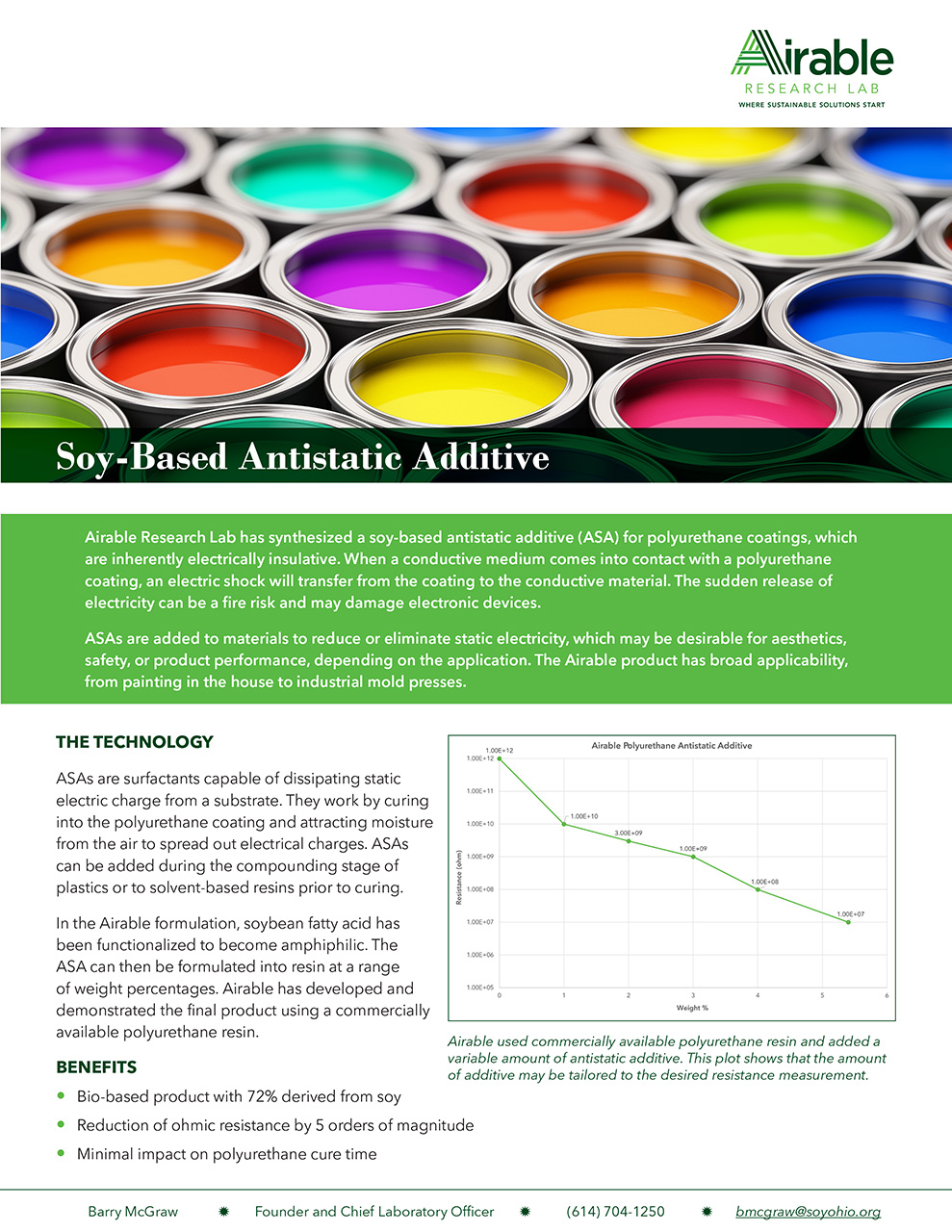
ASAs are surfactants capable of dissipating static electric charge from a substrate. They work by curing into the polyurethane coating and attracting moisture from the air to spread out electrical charges. ASAs can be added during the compounding stage of plastics or to solvent-based resins prior to curing.
In the Airable formulation, soybean fatty acid has been functionalized to become amphiphilic. The ASA can then be formulated into resin at a range of weight percentages. Airable has developed and demonstrated the final product using a commercially available polyurethane resin.
Benefits
- Bio-based product with 72% derived from soy
- Reduction of ohmic resistance by 5 orders of magnitude
- Minimal impact on polyurethane cure time